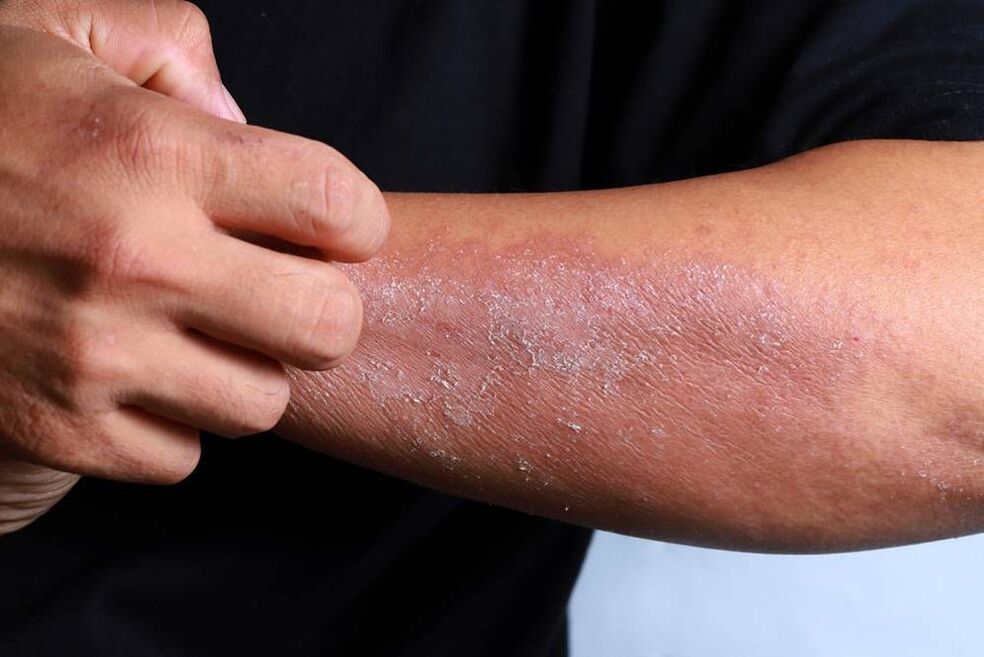
Psoriasisis a chronic inflammatory skin disease. It is a genetic disease that occurs in the form of characteristic formations on the patient's body: pink-red papules or plaques visible on the eye, the surface of which is flaky and covered with scales. The disease is usually accompanied by severe itching and pain, which causes physical and moral suffering to the patients. Psoriasis rashes can appear anywhere on the body, but are most commonly located on the patient's scalp, elbows, and hands. Chronic psoriasis on the head is especially common to cause moral discomfort to patients because it cannot be hidden under clothing.
Where does the name "psoriasis" come from?
The name of the disease "psoriasis" comes from the Greek word - Psora - scratch (-sya). In fact, itching of difficult-to-treat, rough, scaly, silvery-white skin is a typical manifestation of the disease.
Who is affected by this disease?
A disease such as skin psoriasis affects about 3-5% of the population in different countries. Men and women alike. Psoriasis can develop at any age, but usually occurs around the age of 20, often earlier in women than in men. However, Medical On Group has compiled impressive statistics on the treatment of children and the elderly with this disease.
In addition to heredity, psoriasis has the following causes:
- overactive division of skin cells;
- tension;
- decreased immunity after illness.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Is psoriasis contagious?
Common vulgar psoriasis is an inherited, genetic disease associated with metabolic disorders, endocrine glands, and immune system changes. Psoriasis is not contagious! It is not an external infection and there is no need to fear or avoid people who suffer from this suffering.
Is it likely that children of parents with psoriasis also suffer from this disease?
Since we are talking about an inherited genetic disease, there is such a probability, and it is quite high: if both parents suffer from psoriasis, children are about 33. 3% more likely to have this disease.
Is it good for patients to spend as much time in the day as possible?
It is generally accepted that sun exposure contributes to the treatment of psoriasis to some extent, but in some cases, sun exposure can exacerbate the process. Be that as it may, before any medical procedure and if you notice any change in the condition of your skin, it is advisable to consult a qualified dermatologist.
What causes regular outbreaks and disease reduction?
Experience shows that mental stress, stress and neuroses, unhealthy lifestyles and diet cause worsening manifestations of psoriasis. In addition, it is not uncommon for the disease to worsen even more precisely as a result of irrationally formulated treatment.
Does smoking and alcohol consumption affect the course of the disease?
Of course not. Smoking and alcohol consumption have a detrimental effect on the development of the disease and may contribute to the exacerbation of psoriasis.
Treatment of psoriasis. It is possible that?
Hereditary psoriasis of the legs, arms, or head is one of the most common but difficult-to-treat skin conditions. Psoriasis is characterized by a scaly reddening of the skin, the appearance of which is not caused by infection but by increased cell division. In a healthy person, complete regeneration of skin cells occurs in almost a month, and in patients seven times faster.
Exacerbation of psoriasis can be caused by stress and physical overuse, wounds and cuts on the skin, upper respiratory tract streptococcal infection, and medication reactions. Unfortunately, we cannot protect ourselves from all this, which means that medicine is not yet able to prevent or completely cure an attack of the disease. But modern dermatologists are quite capable of controlling the course of psoriasis by choosing effective ways to treat the symptoms.
Can Psoriasis Be Cured Permanently?
Because we are talking about an inherited, genetic disease, the treatment of psoriasis offered by modern medicine means the elimination of the external manifestations of the disease, the long-term cleansing of the patient's skin.